Data quality control (--qc-db)¶
PopPUNK now comes with some basic quality control options, which you should
run on your sketch database made with --create-db by running --qc-db
as follows:
poppunk --qc-db --ref-db example_db --length-range 2000000 3000000
For poppunk_assign, instead add --run-qc:
poppunk_assign --query queries.txt --db example_db --run-qc --max-zero-dist 1 --max-merge 3
The following criteria are available:
Outlying genome length (calculated during sketching, for assemblies or reads) with
--length-rangeand/or--length-sigma.Too many ‘N’s with
--prop-nand/or--upper-n.Outlying core or accessory distances manually with
--max-pi-distand--max-a-distrespectively.Outlying core and/or accessory distances automatically with
--auto-max-dists, with customisable sensitivity--xand resolution--r.Too many zero distances with
--max-zero-dist.
For poppunk --create-db only:
Names of samples to remove (e.g. failing external QC) with
--remove-samples.
For poppunk_assign only:
Maximum number of clusters a single isolate can cause to merge with
--max-merge.Betweenness of queries (not automated, just reported) with
--betweenness.
In all cases a file will be written at qcreport.txt which lists the failing samples, and the
reasons why they failed. Adding --qc-keep will
only write the file and not remove failing samples.
You may also add --retain-failures
to write a separate sketch database with the failed samples.
Random match chances in PopPUNK are only calculated and added to the database after the chosen
QC step. If you use sketchlib directly, they will be added without any automated QC.
QC of input sequences¶
The first QC step is applied directly to the input sequences themselves, to identify poor quality sequences.
You can change the genome length cutoff with --length-sigma which sets the maximum number
of standard deviations from the mean, and --length-range which sets an absolute range of
allowable sizes.
Ambiguous bases are controlled by --prop-n which gives the maximum percentage of Ns,
and --upper-n which gives the absolute maximum value.
QC of pairwise distances¶
The second QC step uses the pairwise distances, to enable the removal of outlier samples that may not be part of the taxon being studied.
By default, the maximum allowed accessory distance is 0.5 to ensure you check for contamination.
However, many species do really have high accessory values above this range, in which case you
should increase the value of --max-a-dist.
The maximum allowed core distance is also 0.5, by default. This can be altered with --max-pi-dist.
Each isolate may have a proportion of distances that are exactly zero as set by
--max-zero-dist.
Genome data from multiple sources could contain misannotated genomes or contamination from closely related species.
PopPUNK provides an automated maximum distance inclusion option to remove the genomes that are likely to
be outliers. To use --auto-max-dists, you would need to specify which distance to do automation (core,
accessory or both).
To determine maximum allowed distances, core and accessory distances are each ordered
and scanned from the 75th percentile onwards. The list of distances is checked in steps of r distances
(default r = 50) for outlier behaviour. If a distance is more than 1 + x (default x = 0.2) times greater
than the distance 1 percent before it, it will be classified as an outlier. The maximum allowed distance
will be selected as the one before the smallest outlier.
Here is an example of automated maximum distance on 5000 Streptococcus pneumoniae genomes sampled from AlltheBacteria database.
Before QC:
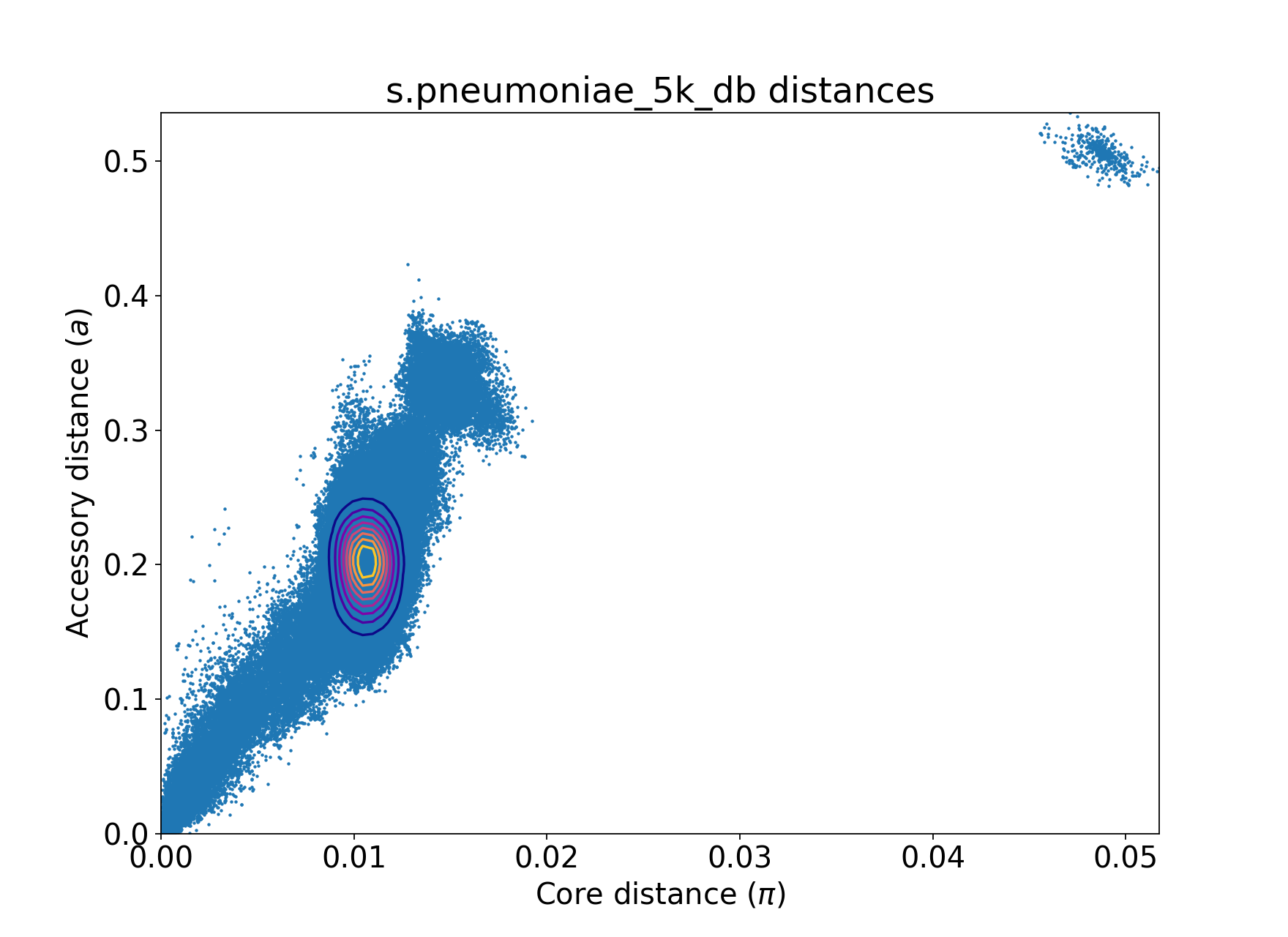
After --auto-max-dists both under default settings:
poppunk --qc-db --ref-db s.pneumoniae_5k_db --output s.pneumoniae_5k_qc_default --auto-max-dists both
PopPUNK (POPulation Partitioning Using Nucleotide Kmers)
(with backend: sketchlib v2.1.4
sketchlib: /Users/apeng/miniconda3/envs/poppunk38/lib/python3.8/site-packages/pp_sketchlib.cpython-38-darwin.so)
Graph-tools OpenMP parallelisation enabled: with 1 threads
Running QC on sketches
Using proportion cutoff for ambiguous bases: 0.1
Using standard deviation for length cutoff: 5
7 samples failed
Detecting maximum distance cutoffs using
x = 0.2, r = 50
Running QC on distances
Using cutoff for core distances: 0.01761072874069214
Using cutoff for accessory distances: 0.3976665222594735
Using cutoff for proportion of zero distances: 0.05
8 samples failed
4986 samples passed QC
Removing 14 sequences
Loading network from s.pneumoniae_5k_db/s.pneumoniae_5k_db_graph.gt
Network loaded: 5000 samples
Recalculating random matches with strand_preserved = False
Calculating random match chances using Monte Carlo
Done
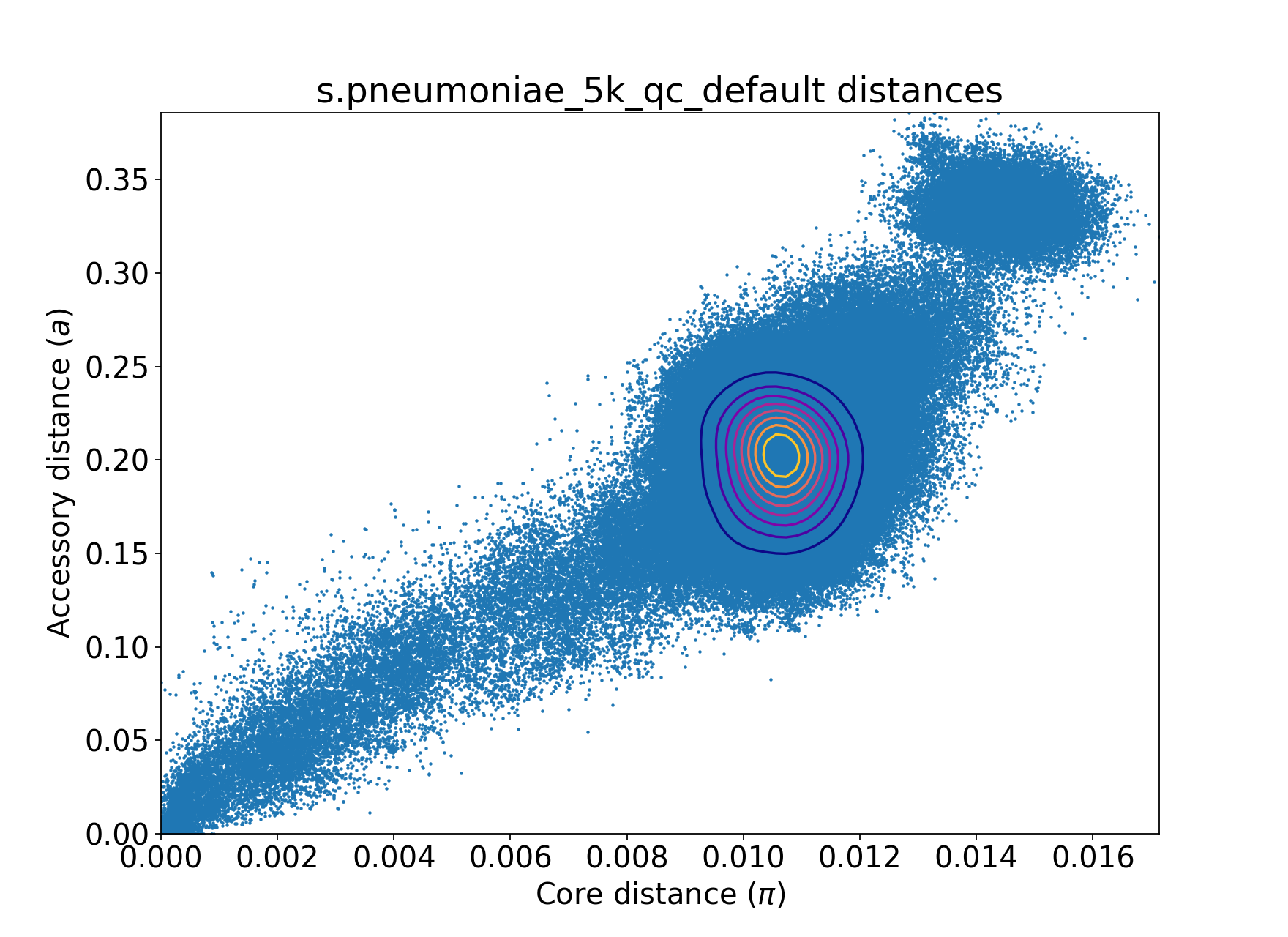
You can tune distance quality control to be more strict by using smaller x. For example, x = 0.1 would remove the S. pneumoniae
cluster at the top right corner, which belongs to a population with a distinct biological feature.
The default r should be enough for datasets of more than 100 genomes. To make sure all outliers are picked out, r / (number of distance pairs)
needs to be smaller than 1 / (number of genomes). You can increase resolution by decreasing r at negligible time cost.
QC of the network (assign only)¶
Finally, you may also check network properties.
Maximum number of clusters a single isolate can cause to merge is
set with --max-merge. More than this number of links across the original clusters
will result in removal of the isolate.
Betweenness of queries can be reported with --betweenness, which may be useful
to prune the input in more complex cases. This does not cause automated removal as
it’s difficult to set a sensible threshold across datasets.
You will therefore need to re-run and remove samples yourself.